Oki became islands about 10,000 years ago, but this is still a short period of time when compared with Sado Island and Tsushima Island, which are also located in the Sea of Japan. Unique creatures whose evolutionary process can be observed live here in Oki, the "young islands."
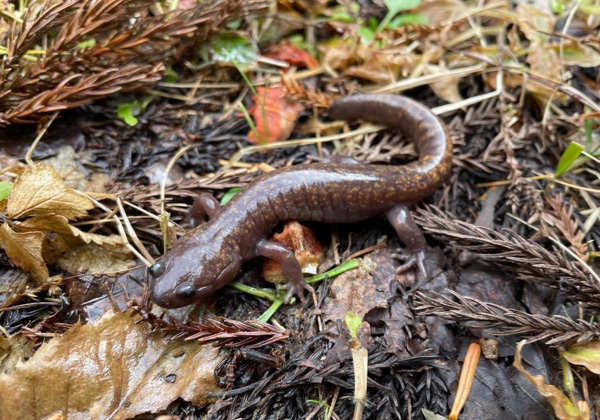

Oki Salamander
Oki salamander (Hynobius okiensis) is a small endemic salamander, found only on Dōgo Island.
It is an endemic species with rare and unique features.
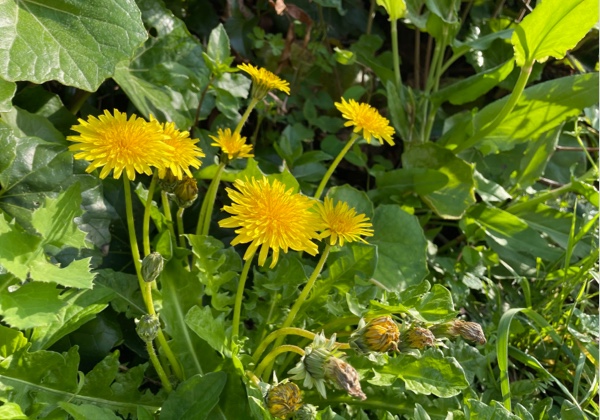

Oki Dandelion
Oki dandelion (Taraxacum maruyamanum) is one of the endemic species that can be seen in many places on the Oki Islands. It is one of the endemic dandelions of Japan, and it can be distinguished from the common dandelion by looking at the calyx (sepal).
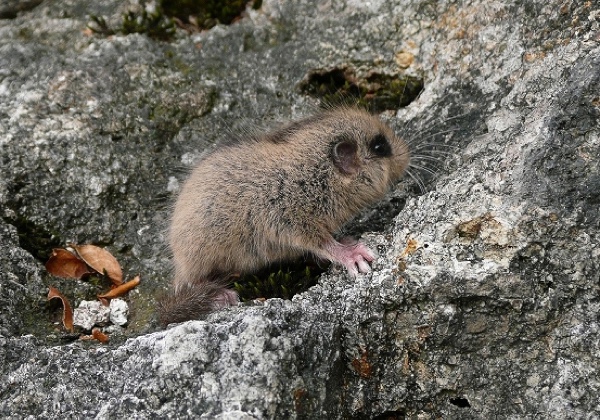

Japanese Dormouse
The Japanese dormouse (Glirulus japonicus), which lives in the mountains on Dōgo Island, is a small mammal which is designated as a Natural Monument of Japan. It is known for its unusual feature of hibernation by lowering its body temperature to almost the same as the temperature of the air outside its nest.